

- #PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY CURVE SIMPLE DEFINITION HOW TO#
- #PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY CURVE SIMPLE DEFINITION FULL#
As consumers’ wants change over time, the PPF shifts to adjust for those changes. For example, if the price of a good increases, producers’ incentive to produce that good will decrease and shift the curve inwards.įinally, changes in consumer preferences can also affect the PPF. Third, changes in the prices of goods and services can cause the curve to shift. An increase in resource availability will cause the curve to move outwards, while a decrease in resource availability will cause it to move inwards. Second, changes in available resources influence how much good producers can make and consequently shift the production possibilities curve. It can be shifted by four major factors: changes in technology, changes in resources, changes in prices, and changes in preferences.įirst, technological advances can lead to an outward shift of the PPC, enabling producers to produce more with the same resources. The four factors that shift the production possibilities curve These assumptions allow economists to predict how production possibilities will change in different scenarios. Production Possibilities Curves assume that only two goods or services represent the whole market. Production Possibilities Curves assume that all resources available are fully employed and none are left idle.
#PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY CURVE SIMPLE DEFINITION FULL#
3rd assumption – Full employment of resources Production Possibilities Curves assume that all resources available remain unchanged and cannot be increased or decreased with more investment. It assumes that the technology used to produce a good or service remains the same and does not improve over time. The four assumptions of a production possibilities curveįour key assumptions were made as follows: 1st assumption – Constant technology

The concept of opportunity cost can explain this: if more resources are devoted to producing one good, fewer will be available for producing another good in other words, it would not be possible to have an infinite supply of both goods. The curve shows the maximum possible amount of one good that could be produced, given a certain production level for the other. Points inside the curve indicate an economy’s current level of inefficiency, meaning it needs to produce at its full potential. Points along this curve show different attainable product combinations given existing resources and technology. The efficient points are represented as a curve with an inward slope because producing more of one good requires sacrificing some production of another good. This is created by plotting two goods on each axis and showing all combinations of those goods that can be produced using all available resources efficiently on a graph. How is the production possibilities curve drawn?
#PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY CURVE SIMPLE DEFINITION HOW TO#
It helps demonstrate the trade-offs that an economy must make when deciding how to allocate resources among various goods and services.īy showing the maximum amount of one good that could be produced with limited resources without affecting the production of another good, the production possibilities curve demonstrates that an economy cannot produce everything it wants. The Production Possibilities Curve, also known as Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF), is an economic model that illustrates the concept of opportunity cost.
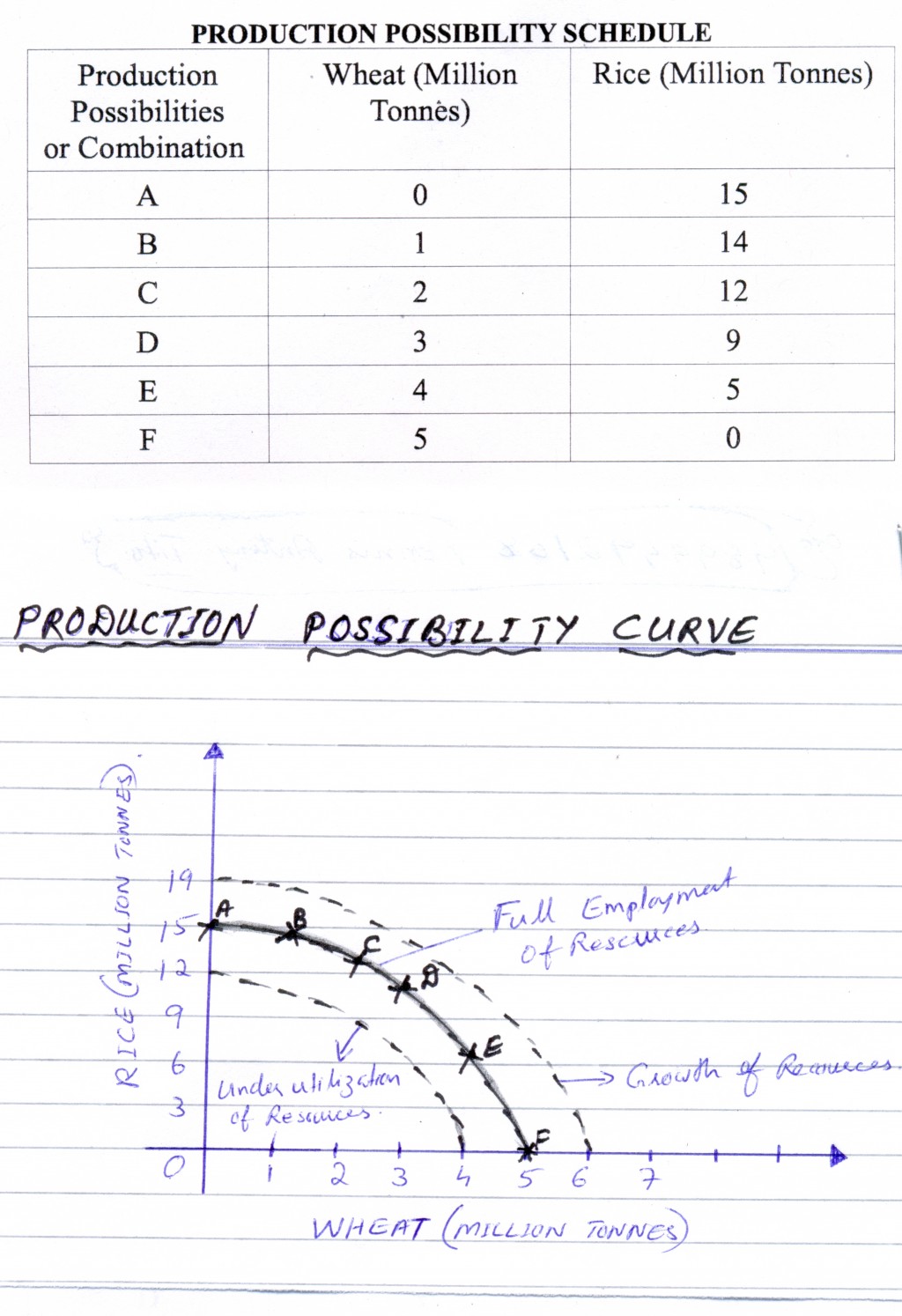
The curve illustrates the concepts of scarcity, choice, opportunity cost, and efficiency. The production possibility curve graphically represents the fusion of two goods that an economy can produce using all its available resources. Limitations What is the production possibility curve?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
